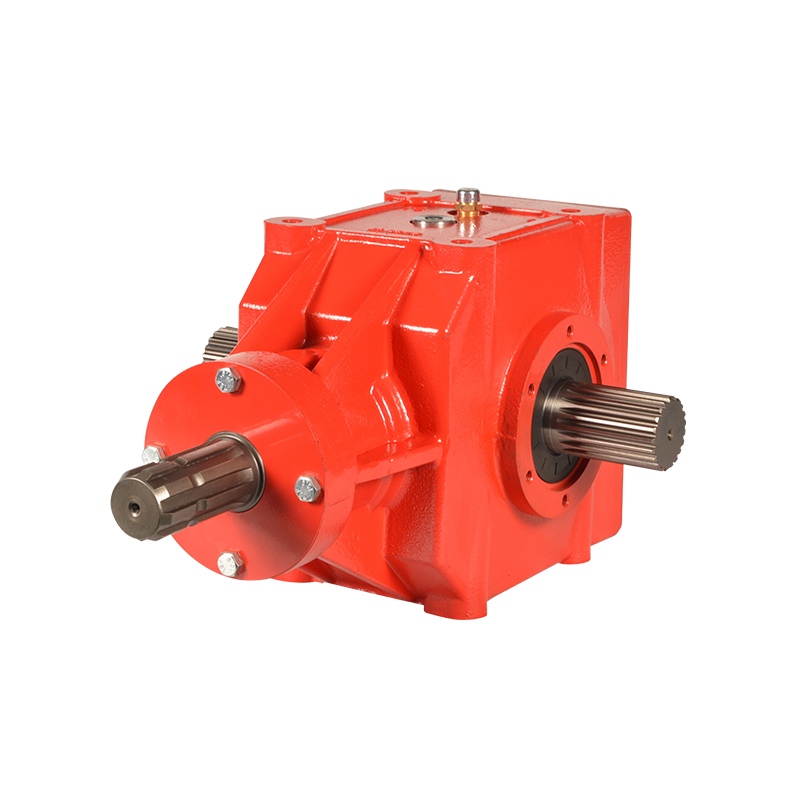
KLF-DXB220 Power driven rake transmission Gearbox
Cat:Grader Driven Rake Gear Box
This product is used in the power-driven rake main transmission gearbox. It is derived from European and American design concepts. The main transmissi...
See DetailsSnow blowers are essential tools in regions that experience harsh winter conditions. They allow homeowners and professionals to clear driveways, sidewalks, and large open areas efficiently. While the visible parts of a snow blower, such as the auger and chute, often receive the most attention, the gearbox plays a crucial role in the machine’s performance. A snow blower gearbox is responsible for transferring power from the engine to the auger and impeller, enabling the machine to handle even the heaviest snow loads with consistency and efficiency.
The gearbox is the mechanical heart of a snow blower. It connects the engine’s power output to the rotating components that move snow. Typically made of durable metals such as aluminum or steel, a gearbox contains gears, shafts, bearings, and lubrication systems designed to manage torque and rotational speed. In single-stage and two-stage snow blowers, the gearbox ensures that the auger spins at an optimal speed to gather and discharge snow while preventing strain on the engine.
In heavy snow conditions, the gearbox must transfer high amounts of torque efficiently. Torque is the rotational force generated by the engine, which must overcome resistance from snow and ice. The gearbox achieves this through a combination of gear ratios, which adjust the speed and force delivered to the auger and impeller. Properly designed gearboxes allow snow blowers to maintain consistent operation even when encountering compacted snow or icy surfaces.
A snow blower gearbox is engineered to handle variable loads. Some key design features contribute to its effectiveness:
Gear Material and Construction: High-quality steel or alloy gears provide strength and durability. Hardened teeth reduce wear over time and prevent breakage under heavy stress.
Gear Ratios: Snow blower gearboxes use specific gear ratios to balance speed and torque. Lower gear ratios provide higher torque, which is crucial when clearing dense snow, while higher ratios allow for faster clearing of lighter snow.
Sealed Bearings and Lubrication: Bearings inside the gearbox reduce friction and allow smooth rotation of shafts and gears. Sealed or lubricated bearings prevent moisture and snow from causing corrosion, ensuring long-term reliability.
Reinforced Housing: The gearbox housing protects internal components from snow, ice, and debris. A robust housing design reduces the risk of damage when the auger encounters hard surfaces such as pavement or packed snow.
These design elements work together to ensure that the gearbox can deliver consistent performance without overheating or failing, even under challenging conditions.
When a snow blower encounters heavy snow, the resistance against the auger increases significantly. The gearbox manages this by distributing engine power efficiently and adjusting torque as needed. The process involves several mechanical principles:
Torque Transmission: The engine generates torque that is transferred through the gearbox to the auger and impeller. The gears inside the gearbox multiply or reduce torque depending on the load. Heavy, wet, or icy snow requires higher torque to maintain auger rotation.
Speed Regulation: Gear ratios also control the speed at which the auger spins. Slower rotation provides greater force, preventing the auger from stalling when encountering dense snow. Conversely, lighter snow can be cleared more quickly using higher-speed settings.
Load Distribution: Gearboxes distribute stress evenly across gears and shafts. High-quality gearboxes prevent a single component from bearing excessive load, reducing the risk of mechanical failure.
Shock Absorption: Some snow blower gearboxes are designed with flexible or slip-clutch mechanisms that absorb sudden shocks. For example, if the auger hits a hidden rock or hard ice, the gearbox temporarily slips to protect the gears from damage.
Despite their robust design, snow blower gearboxes can encounter problems if not properly maintained or if used in extreme conditions repeatedly. Common issues include:
Gear Wear and Damage: Repeated exposure to high torque loads can wear down gear teeth over time. Hardened or alloy gears resist wear, but eventually, even the best materials degrade.
Bearing Failure: Bearings can fail due to contamination from snow, ice, or dirt. Lack of lubrication accelerates wear and increases friction, leading to overheating.
Lubrication Loss: Gearboxes require proper lubrication to function efficiently. If seals are damaged or lubricant levels are low, friction increases, which can cause premature wear and even gear seizure.
Housing Cracks: Extreme impact, such as hitting hard ice or rocks, can crack the gearbox housing. Cracks allow moisture to enter, accelerating corrosion and internal damage.
Understanding these issues allows users to prevent them through regular inspection, cleaning, and maintenance.
Maintaining a snow blower gearbox is essential for handling heavy snow efficiently and extending the life of the machine. Key maintenance practices include:
Regular Inspection: Check for signs of wear on gears, bearings, and shafts. Look for cracks in the housing and ensure that bolts and fasteners are tight.
Lubrication: Follow manufacturer guidelines for gear lubricant types and replacement intervals. Regular lubrication reduces friction, wear, and the risk of overheating.
Cleaning: Remove accumulated snow, ice, and debris from the gearbox area. Moisture can cause corrosion, especially if the gearbox housing is compromised.
Seasonal Servicing: Before and after the winter season, inspect the gearbox thoroughly. Replace worn parts, check bearings, and ensure all components operate smoothly.
Avoid Overloading: Clearing extremely dense or deep snow in a single pass can strain the gearbox. Multiple passes with moderate loads reduce stress and prevent damage.
Modern snow blowers incorporate advanced gearbox designs to improve performance under heavy snow loads. Some innovations include:
Slip Clutch Mechanisms: These protect the gearbox by allowing the auger to slip when encountering resistance beyond normal limits. This reduces the likelihood of gear breakage.
Improved Lubricants: Synthetic and high-performance lubricants maintain viscosity at low temperatures, ensuring smooth operation even in extreme cold.
Sealed and Shielded Designs: Enhanced sealing prevents moisture, ice, and debris from entering the gearbox, reducing maintenance requirements and prolonging lifespan.
Lightweight Alloys: Some gearboxes use high-strength lightweight alloys, reducing overall weight while maintaining durability, making snow blowers easier to maneuver without sacrificing performance.
The snow blower gearbox is an often-overlooked but critical component that allows machines to handle heavy snow loads efficiently. By transmitting torque, regulating speed, distributing load, and absorbing shocks, the gearbox ensures reliable and consistent performance in challenging winter conditions. Proper design, maintenance, and understanding of how the gearbox works are essential to maximize the efficiency and lifespan of a snow blower.
Regular inspection, lubrication, and careful operation prevent common issues such as gear wear, bearing failure, and housing damage. Modern innovations, including slip clutches, advanced lubricants, and improved sealing, further enhance gearbox reliability and performance.
Whether clearing a driveway or managing larger areas of snow accumulation, understanding and maintaining the snow blower gearbox ensures that your machine can handle heavy snow loads safely, efficiently, and effectively for many winters to come.